Architecture design and verification test of highly available databases for three centers geographically dispersed in two locations
-
摘要:
目前,两地三中心已成为大型企业数据中心建设的主要模式,为企业提供更加安全、稳定、高效的信息化平台,保障企业信息系统安全高效运营,满足不同故障和灾难场景下对业务连续性的要求。基于开源的关系型数据库管理系统PostgreSQL和开源的分布式协调服务ZooKeeper,文章设计了一种两地三中心高可用数据库架构,能够实现分布式事务一致性及故障场景下数据库高可用,并通过故障场景测试用例对其进行验证测试。测试表明,按照该架构设计部署的两地三中心数据库,当常见故障发生时,数据库均可自动进行故障隔离,且数据零丢失,能够持续稳定地提供数据访问服务,不会影响到上层业务。该数据库架构设计节约软件成本,透明可靠、安全性高,并可针对实际需要进行定制。另外,数据存储介质使用的是服务器本地盘而非集中存储,有利于降低数据库建设成本和运维成本。
Abstract:At present, three centers geographically dispersed in two locations have become the main mode for the construction of large enterprise data centers, providing enterprises with a more secure, stable, and efficient information platform, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of enterprise information systems, and meeting the requirements for business continuity in different fault and disaster scenarios. Based on the open-source relational database management system PostgreSQL and the open-source distributed coordination service ZooKeeper, this article proposes a design of the architecture of highly available databases for three centers geographically dispersed in two locations, which can achieve distributed transaction consistency and high availability of the database in fault scenarios. Test cases of common fault scenarios are conducted to verify the design and it is shown that the databases for three centers geographically dispersed in two locations deployed according to this architecture can automatically perform fault isolation with zero data loss when common faults occur, and can provide continuous and stable data access services without affecting upper level business. The database architecture design is cost-saving in software , transparent, reliable, and highly secure, and can be customized according to actual needs. In addition, the use of server local disks instead of centralized storage as data storage media is beneficial for reducing database construction and operation costs.
-
随着云计算和大数据技术的广泛应用,企业信息系统集中化部署成为主流趋势。为保障企业信息系统安全高效运营,满足不同故障和灾难场景下对业务连续性的要求,为企业提供更加安全、稳定、高效的信息化平台,两地三中心已成为企业数据中心建设的共识。数据库作为信息系统的重要组成部分,需要解决高并发、海量数据访问、持续提供服务、数据安全等越来越复杂的问题[1],高可用数据库设计与实现是两地三中心建设的一项关键任务[2]。
高可用是信息系统提供连续性业务服务的一种能力。高可用数据库架构设计需要综合考虑如何避免因服务器、网络及软件等发生故障而造成业务服务不可用。实现两地三中心数据库的高可用有多种途径,各大厂商纷纷提出各自的数据库高可用解决方案。以TiDB为代表的云原生分布式数据库解决方案,基于分布式一致性算法,保障了集群数据的一致性和高可用,但对数据中心之间的网络延时有较高要求;以Oracle为代表的集中式数据库解决方案,通过数据同步软件实现数据在多个数据中心之间的实时逻辑复制,但在主数据库发生故障时可能存在数据丢失情况。
本文借鉴商用数据库高可用解决方案和国内外相关研究,设计一种基于开源关系型数据库管理系统PostgreSQL和开源分布式协调服务ZooKeeper的两地三中心数据库高可用架构,并进行了验证测试。
1 两地三中心数据库架构
两地三中心通常由同城的2个数据中心(即同城一中心和同城二中心)和1个异地的灾备中心构成。
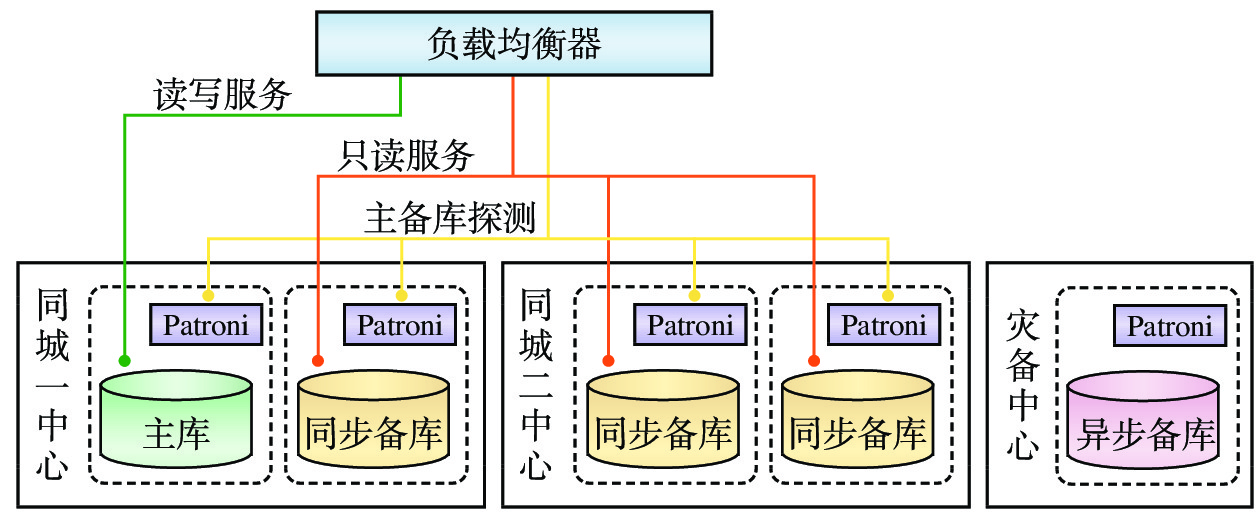
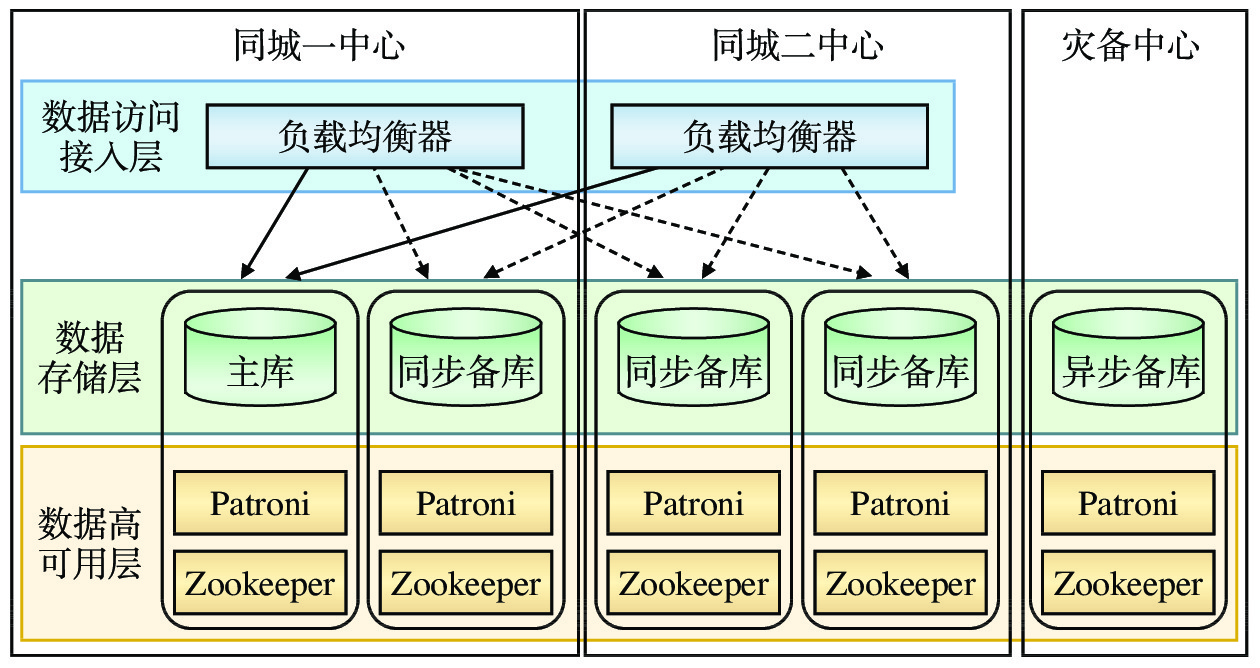
两地三中心数据库划分为3个层次:为业务提供服务的数据访问接入层、负责数据存储的数据存储层、实现数据库高可用保障的数据高可用层,其架构如图1所示。
Patroni是PostgreSQL的一个开源HA工具,用于检测各个数据库节点的状态和配置,并负责数据库的故障切换。Zookeeper是一个开源的分布式协调服务,用于管理数据库集群,负责存储数据库节点的状态和配置。
1.1 数据访问接入层
数据访问接入层是面向应用的数据访问接口,根据应用需求提供数据库读/写服务。
数据访问接入层主要由负载均衡器组成,其工作过程如图2所示。
负载均衡器通过Patroni的接口获取数据库的状态信息,确定可提供数据读写服务的数据库主库和仅提供数据读服务的数据库备库[3]。同城中心的3个备库与主库始终保持同步更新,存储的数据完全一致;而灾备中心备库以异步方式更新数据,存储的数据相比主库有一定延迟。正常情况下,负载均衡器不对灾备中心的异步备库进行探测,仅从数据完全一致的同城中心选择同步备库对外提供服务。
负载均衡器实时对同城中心数据库节点进行探测,可获4个数据库节点的主备状态。当数据库主备库发生切换时,负载均衡器快速进行流量切换,将业务流量切换至正确的数据库,屏蔽数据库切换对上层业务的影响,为上层业务提供持续稳定的数据访问服务。
1.2 数据存储层
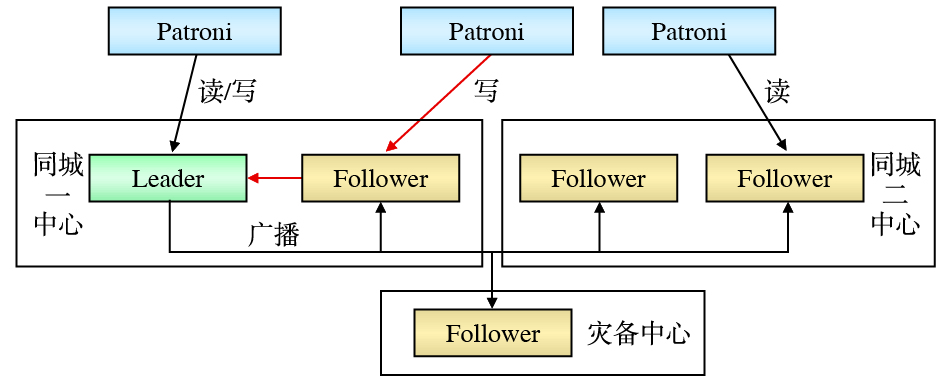
数据存储层作为数据存储的载体,采用基于PostgreSQL数据库的5节点数据副本模式,即两个同城数据中心各部署2个数据库节点,灾备中心部署1个数据库节点,每个数据库节点部署1个具有全部数据的数据副本[4]。数据库的主库由两个同城中心通过选举产生,主库对外提供数据读写服务,备库仅提供数据读服务。异地灾备中心主要用于数据异地备份,正常情况下不会被选举为主库。数据库的主库到同城的3个备库采用同步复制模式,确保一个同城中心整体发生故障时,另一个同城中心仍具有全部业务数据,且故障恢复后不丢失数据(即RPO为0)。同时,当备库发生故障时,主备库间的同步复制自动降级为异步复制[5]。为了降低数据复制对数据库系统的性能影响,主库到灾备中心的备库采用异步复制模式。
为了保障业务服务的连续稳定和数据同步的安全高效,数据存储层将南北向流量(即数据中心外部用户和内部服务器之间交互的流量)和东西向流量(即数据中心内部不同服务器之间交互的流量或不同数据中心之间的网络流量)进行逻辑隔离,南北向的业务流量采用业务网,东西向的数据同步流量采用数据同步网。
1.3 数据高可用层
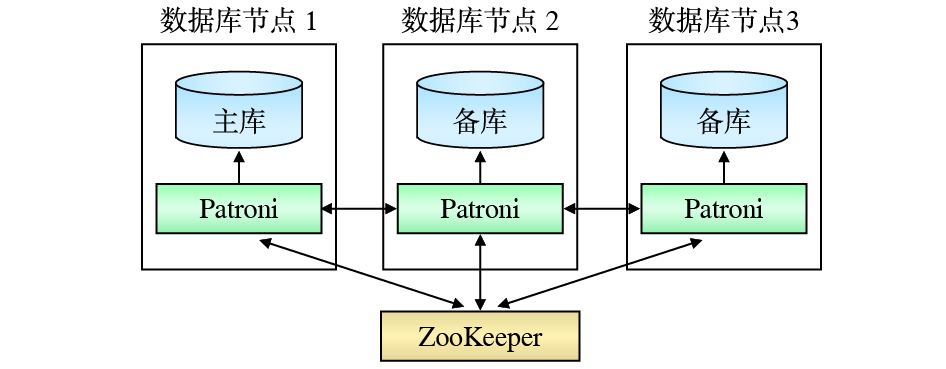
数据库高可用层采用Patroni+集群状态信息配置存储服务(DCS,Distributed Configuration System)的组合模式。Patroni运行在每个数据库节点上,通过探测数据库节点及数据副本的状态来进行数据库主备切换。DCS负责存储数据库节点的状态信息,为Patroni的数据库主备切换决策提供依据,采用基于ZooKeeper的分布式数据一致性解决方案。ZooKeeper采用与数据存储层相同的5节点集群部署模式,分别部署在数据副本驻留的数据库节点上,通过ZooKeeper原子广播(ZAB,ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)协议来保障服务高可用。
2 关键技术
2.1 分布式事务一致性实现
在两地三中心数据库集群上实现分布式事务一致性是实现数据库高可用的基础。基于ZooKeeper的分布式事务一致性解决方案采用多副本方式,天然适用于两地三中心架构。ZooKeeper能够保障事务请求的顺序一致性、原子性、单一视图性、可靠性及实时性。
(1)顺序一致性:同一个客户端发起的事务请求将按照发送的顺序被写入到ZooKeeper。
(2)原子性:所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有节点上的执行情况完全一致,即整个集群所有节点都成功地执行了某一个事务,或都不执行。
(3)单一视图性:客户端连接到任一ZooKeeper服务器,看到的服务端数据模型都是一致的。
(4)可靠性:一旦服务端成功地执行一个事务,并完成对客户端的响应,该事务所引起的服务端状态变更会被一直保留下来。
(5)实时性:ZooKeeper可确保在一定时间段内,客户端能够从服务端读取到最新数据状态[6]。
ZooKeeper使用ZAB协议。ZAB协议是为分布式协调服务ZooKeeper设计的一种支持崩溃恢复的原子广播协议,基于该协议ZooKeeper可实现多个副本间数据一致性。ZooKeeper定义有3种角色的节点:Leader、Follower和Candidate。在选举过程中,一个节点只要求获得半数以上投票,即可当选为Leader。Leader节点负责处理客户端的写请求并进行消息广播,当收到一个写请求后,将其广播给各个Follower节点,当一半以上Follower节点应答之后,Leader节点再向各Follower节点发送Commit命令,告知其提交相关事务[7]。Candidate 仅出现在 Leader 选举过程中,如果 Follower副本在一段时间内没有收到 Leader 副本的心跳,则判断 Leader 可能已经故障,此时启动选主过程,副本会变成 Candidate,直到选主结束。一旦Leader节点出现网络中断、崩溃、退出与重启等异常情况时,ZAB协议就会进入恢复模式,并通过选举产生新的Leader。采取这种工作机制,ZooKeeper集群中只要有超一半的节点存活,集群就可对外提供服务。
两地三中心ZooKeeper集群部署如图3所示。Patroni通过Leader节点将数据直接写入ZooKeeper集群,也可通过Follower节点将数据传递至Leader节点,再由Leader节点写入ZooKeeper集群,通过Leader或Follower读取ZooKeeper集群中的数据。
2.2 数据库高可用保障
数据库高可用是由ZooKeeper和Patroni共同保障的,其工作机制如图4所示。ZooKeeper集群负责数据库主备节点状态及配置等信息的存储。Patroni负责监控和控制本地数据库,周期性地检测本地数据库节点状态,将数据库节点状态记录在ZooKeeper集群中,同时读取最新的配置信息和集群状态,当发现主数据库故障后自动进行主备切换[8]。
拥有Leader密钥的数据库作为主数据库,主数据库的Patroni会定期向ZooKeeper发送更新Leader密钥的请求[9];当主数据库异常导致Patroni无法及时更新Leader密钥时,Leader密钥就会过期,从而触发新的选举。数据库主备切换流程为:
(1)主数据库发生故障,导致Leader密钥被删除,处于健康且存活状态的所有备数据库会发起对Leader密钥的争夺。Patroni之间可互相访问,先与原来的主数据库进行通信,当发现访问超时,则访问ZooKeeper查询数据库集群状态,向满足选举条件的Patroni发送创建密钥的请求,抢到Leader密钥的数据库成为新的主数据库
(2)故障数据库节点恢复后,发现集群已拥有主数据库,会自动降级成为一个备数据库。
3 验证测试
3.1 测试环境
搭建两地三中心数据库的测试环境需要综合考虑数据中心位置、网络条件、计算及数据存储等多方面因素。
(1)数据中心位置:本文测试环境选择的两个同城数据中心相距约10 km,两个同城数据中心到灾备中心的距离均超过100 km。
(2)网络连接:数据中心内部均采用万兆网络互联,两个同城数据中心之间采用千兆网络专线互联,保障两个同城中心之间具有较大的带宽和较小的网络延迟,以满足两个同城中心的主库和备库间的同步数据复制需求。同城数据中心与灾备中心采用千兆网络互联,在实际生产中采用此方式可降低经济成本。同时,为业务网和数据同步网配置独立且相互隔离的网络地址段。数据中心内部及两个同城中心间网络延迟在2 ms以内,同城中心到灾备中心网络延迟在8 ms以内。
(3)计算及数据存储:采用物理服务器+本地盘存储的数据库部署模式[10],而不是传统物理服务器+集中存储的数据库部署模式。传统的数据库部署模式采用集中存储主要是为了提高数据读写性能,并利用集中存储硬件的冗余保护来保障数据存储的安全性。而两地三中心数据库采用本地SSD盘存储数据,既可满足数据库的读写性能要求,采用多副本存储还能够提高数据的安全性。数据库采用物理服务器+本地盘存储的部署模式,可降低复杂度,并有助于降低建设成本及后期运维成本[11]。
3.2 故障场景测试用例
为了模拟较为复杂的生产场景,将主数据库置于一个同城数据中心(同城一中心),ZooKeeper Leader置于另一个同城数据中心(同城二中心)。
生产环境中常见的故障有服务器硬件故障、数据库故障、业务网故障、数据同步网故障及极端情况下的整个数据中心故障[12]。根据生产环境中常见的故障,设计了12种故障场景测试用例:
(1)两个同城中心间业务网异常;
(2)两个同城中心间数据同步网异常;
(3)同城二中心与同城一中心、灾备中心间数据同步网均异常;
(4)同城一中心与同城二中心、灾备中心间数据同步网均异常;
(5)灾备中心与同城一中心、同城二中心间数据同步网均异常常;
(6)三个中心数据同步网全部异常;
(7)同城一中心整体故障;
(8)同城二中心整体故障;
(9)灾备中心整体故障;
(10)同城一中心与同城二中心整体故障;
(11)同城一中心与灾备中心整体故障;
(12)同城二中心与灾备中心整体故障。
4 测试结果及结论
4.1 测试结果
(1)两个同城中心间业务网异常
数据同步网正常,ZooKeeper集群正常,数据库集群正常。同城二中心数据访问接入层因无法连接到主库,仅能提供读服务,无法提供写服务,而同城一中心可正常提供服务。
(2)两个同城中心间数据同步网异常
同城一中心ZooKeeper无法连接到ZooKeeper Leader,故脱离集群。ZooKeeper集群仍有3个节点正常运行,故集群仍可正常提供服务。同城一中心的主库可访问灾备中心ZooKeeper,故主库正常。同城二中心所有数据节点无法连接到同城一中心主数据节点,致使同城二中心的同步备库降级为异步备库,但并未脱离集群,在降级过程中,数据库短暂停止服务,业务闪断后恢复正常。
(3)同城二中心与同城一中心、灾备中心间数据同步网均异常
同城二中心ZooKeeper无法连接到同城一中心和灾备中心的ZooKeeper,成为少数派脱离集群,ZooKeeper Leader重新在同城一中心和灾备中心选举产生,重新选举Leader对业务无影响。同城二中心所有数据库无法连接到新的ZooKeeper集群,致使同城二中心数据库脱离集群,同时同城一中心主库到同城二中心备库的同步复制降级为异步复制,在降级过程中,数据库短暂停止服务,业务闪断后自动恢复正常。
(4)同城一中心与同城二中心、灾备中心间数据同步网均异常
同城一中心ZooKeeper无法连接到同城二中心和灾备中心的ZooKeeper,成为少数派脱离集群,此时ZooKeeper变为3节点集群,Leader无需切换,可正常提供服务。同城一中心主备库均无法连接到ZooKeeper集群,致使同城一中心数据库脱离集群,此时同城二中心的一个同步备库升级为主库,在主备切换的过程中,数据库短暂停止服务,业务闪断后自动恢复正常。
(5)灾备中心与同城一中心、二中心间数据同步网均异常
灾备中心ZooKeeper无法连接到同城一中心和二中心的ZooKeeper,成为少数派脱离集群,此时ZooKeeper变为4节点集群,Leader无需切换,可正常提供服务。灾备中心数据库均无法连接到ZooKeeper集群,致使灾备中心数据库脱离集群。业务网正常,同城一、二中心数据访问接入层均可正常提供读写服务,业务不会受到影响。
(6)三个中心数据同步网全部异常
当三个中心数据同步网全部异常,ZooKeeper集群无法正常运行,此时数据库集群无法正常运行,需要人工干预,将某一数据库提升为主库。
(7)同城一中心整体故障
同城一中心ZooKeeper脱离集群,此时ZooKeeper变为3节点集群,Leader无需切换,可正常提供服务。同城一中心数据库脱离集群,同城二中心一个同步备库升级为主库,当发生主备切换时,数据库短暂停止服务,业务闪断后自动恢复正常。
(8)同城二中心整体故障
同城二中心Zookeeper脱离集群,ZooKeeper Leader重新在一中心和灾备中心选举产生,Leader的重新选举对业务无影响。同城二中心数据库脱离集群,同城一中心数据库正常,无需切换主备库,但同城一中心主库到二中心备库的同步复制降级为异步复制,在降级过程中,数据库短暂停止服务,业务闪断后自动恢复正常。
(9)灾备中心整体故障
ZooKeeper 集群仍有 4 个节点正常运行,故集群仍可正常提供服务,两个同城数据库节点均正常,业务不会受到影响。
(10)同城一中心与同城二中心整体故障
ZooKeeper 集群无法正常工作,此时数据库集群无法正常运行,需要人工干预,将灾备中心数据库节点提升为主库。
(11)同城一中心与灾备中心整体故障
ZooKeeper 集群剩余节点不超过总节点数的50%,此时数据库集群无法正常运行,需要人工干预,将同城二中心一个数据库节点提升为主库。
(12)同城二中心与灾备中心整体故障
ZooKeeper 集群剩余节点不足一半总节点数,此时数据库集群无法正常运行,需要人工干预,将同城一中心一个数据库节点提升为主库。
4.2 测试结论
通过对本文提出的两地三中心数据库的测试与分析,可得到以下结论:
(1)当两个同城中心间发生网络故障时,无论是业务网或数据同步网故障,业务几乎不会受到影响,系统服务恢复时间(RTO,Recovery Time Objective)约为0,恢复点目标(RPO,Recovery Point Objective)为0。但业务网故障时,仅有一个同城中心的数据访问接入层可提供服务。
(2)当任一同城数据中心数据同步网或整体发生故障时,业务几乎不会受到影响,RTO 约为 0,RPO 为 0;当灾备中心数据同步网或整体发生故障时,业务不会受到影响,RTO为 0,RPO 为 0。
(3)当两个同城数据中心同时发生故障或数据同步网整体发生故障时,由于 ZooKeeper 集群无法正常工作,此时业务会受到影响,需要人工干预来恢复业务。
5 结束语
本文提出一种用于两地三中心的高可用数据库架构,能够实现分布式事务一致性及故障场景下数据库高可用;并结合实际生产过程中可能出现的故障,设计了12种故障场景测试用例进行验证。结果表明,按照该架构部署两地三中心数据库,除了两个同城数据中心同时发生故障或者数据同步网整体发生故障的情况外,其它故障发生时,数据库均可自动进行故障隔离,且数据零丢失,能够持续稳定地提供数据访问服务,不会影响到业务。该数据库架构使用了开源的关系型数据库管理系统PostgreSQL和开源的分布式协调服务ZooKeeper,不但节约软件成本,透明可靠、安全性高,还可针对实际需要进行定制。此外,数据存储介质使用的是服务器本地盘而非集中存储,有利于降低数据库建设成本和运维成本。
本文提出的两地三中心高可用数据库架构中,ZooKeeper集群对网络传输的稳定性具有一定的要求,数据中心间的网络抖动会对数据库的高可用产生一定的影响,下一步将继续优化数据库集群的网络设计,降低网络对数据库高可用性的影响。
-
[1] 李保旭. 北京农商银行两地三中心多活容灾的探索与实践[R]. 北京:北京农村商业银行股份有限公司,2018. [2] 董 帅,孙杭标,陈跃俊. Oracle数据库容灾备份系统的建设研究[J]. 网络安全技术与应用,2023(7):61-62. [3] 锁向荣,齐 胜,张悦斌,等. 铁路云平台细粒度访问控制方案研究[J]. 铁路计算机应用,2021,30(4):45-49. [4] 贺 楠. 大数据环境下的数据库备份与恢复策略研究[J]. 信息与电脑,2023,35(8):179-181. [5] 韩 媛,王占昌,杨 博,等. 浅谈基于Postgres-XL的分布式地质大数据集群架构[J]. 中国矿业,2017,26(S1):83-86,91. [6] 钟佳霖. 基于Zookeeper的分布式电力系统状态估计[D]. 济南:济南大学,2022. [7] 陈 涛,索海燕. Apache ZooKeeper设计理念和数据结构的研究[J]. 现代计算机,2022,28(21):63-68. [8] Pedroso M B P .High Availability and Load Balancing for Postgresql Databases : Designing and Implementing[J].International Journal of Database Management Systems,2016, 8(6): 27-34.
[9] 陈玉林,王 武. Zookeeper分布式锁的4种异常状态分析[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护,2019(9):28-29. 陈玉林, 王 武. Zookeeper分布式锁的4种异常状态分析[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护, 2019(9): 28-29.
[10] 王启明,王 健. 基于非共享存储的系统高可用集成方案的实现[J]. 铁路计算机应用,2017,26(5):34-37. [11] 沈萍萍,关 辉,韦 阳,等. 分布式集群系统架构设计及应用部署[J]. 信息技术与信息化,2021(1):159-162 沈萍萍, 关 辉, 韦 阳, 等. 分布式集群系统架构设计及应用部署[J]. 信息技术与信息化, 2021(1): 159-162
[12] 金 燕,李 静,雷 鸣,等. 试验测试数据管理系统设计与实现[J]. 国外电子测量技术,2020,39(2):123-126. DOI: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.1901746. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 许海荣. CR200J3型动力集中动车组空调故障分析及改进. 铁道车辆. 2025(02): 184-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: