Train positioning simulation system for GNSS dead zone in rail transit line
-
摘要: 全球卫星导航系统(GNSS,Global Navigation Satellite System)能够提供实时、高精度列车定位服务,采用基于GNSS的列车定位技术可减少列车运行控制系统的轨旁设备,简化车载设备,有利于降低轨道交通运营维护成本。对于地形地貌复杂、隧道较多的轨道交通线路,可能存在GNSS信号盲区,GNSS无法为运行列车连续提供可靠的列车定位信息,影响了基于GNSS的列车定位技术的应用。为此,文章采用软件无线电技术,开发了轨道交通线路GNSS信号盲区列车定位模拟系统,能够为线路上GNSS信号盲区生成列车定位模拟信号,使列车在经过GNSS信号盲区时能够获取到准确的列车定位数据,有利于扩大基于GNSS的列车定位技术的应用范围。在实验室内搭建测试环境,运行该系统生成单点静态定位模拟信号和区段动态定位模拟信号,与现场采集的卫星定位信号进行对比,验证该系统的可行性和有效性。
-
关键词:
- 轨道交通 /
- 列车定位 /
- 全球卫星导航系统(GNSS) /
- 软件无线电 /
- 仿真系统
Abstract: The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) can be used to provide real-time and high-precision train positioning services. The application of GNSS-based train positioning technology can help reduce the trackside equipment of the train operation control system and simplify its onboard equipment, which is conducive to reducing the operation and maintenance costs of rail transit. For rail transit lines with complex terrain and numerous tunnels, there may be GNSS signal blind zones within which the GNSS cannot provide reliable train positioning data continuously for running trains, affecting the application of GNSS based train positioning technology. Therefore, the article adopts software defined radio technology to develop a train positioning simulation system for GNSS signal blind zones in rail stransit lines. The simulation system can generate train positioning simulation signal for GNSS signal blind zones in the line, so that trains can obtain accurate train positioning data when passing through GNSS signal blind zones, which is conducive to expanding the application scope of GNSS based train positioning technology. After building a testing environment in the laboratory, the system is run to generate static train positioning simulation signal for a single point(i.e.a station) and dynamic train positioning simulation signal for a section, and compare the simulation signals with satellite positioning signals collected on site to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the system. -
-
表 1 L1信号参数值
参数 值 码型 C/A码(粗捕获码) 调制方式 二进制相移键控(BPSK) 频率 1575.42 MHz 码速率 1.023 MHz 表 2 BRDC文件名规则
符号 意义 DDD 数据观测时间的年积日 yy 年份 t 文件种类,一般为n,表示广播星历文件 表 3 实验室条件下生成的GPS定位模拟信号测量值
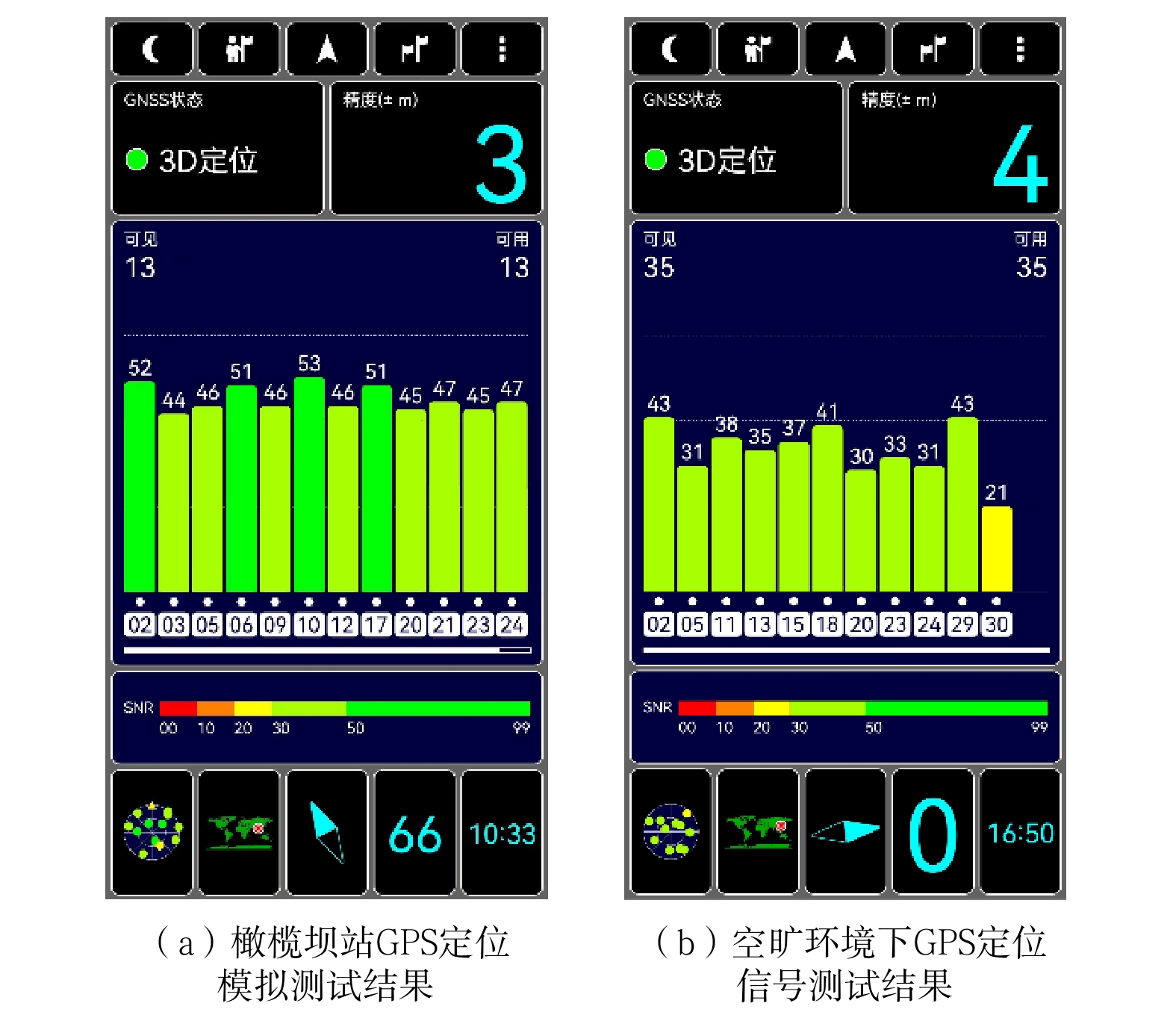
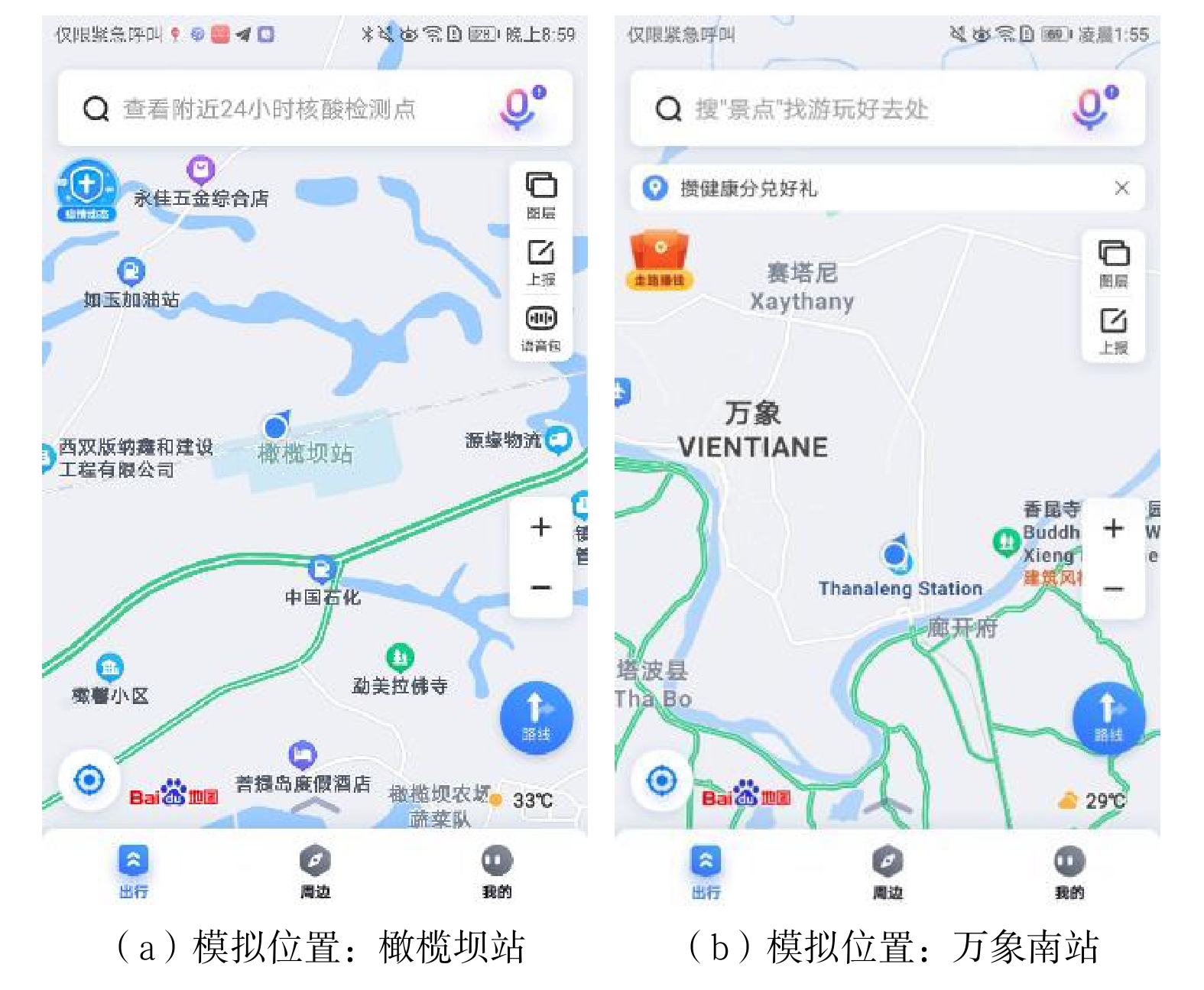
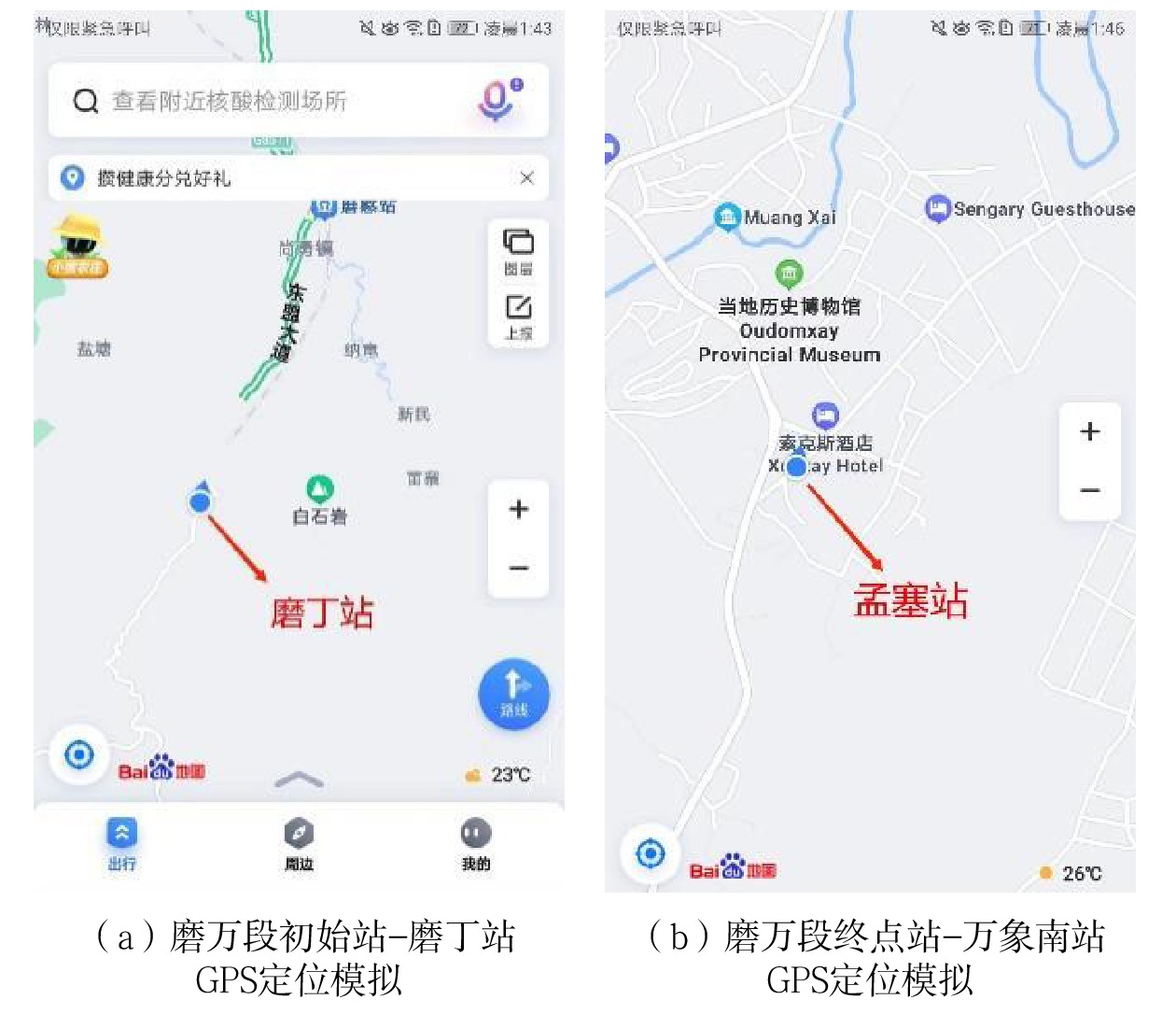
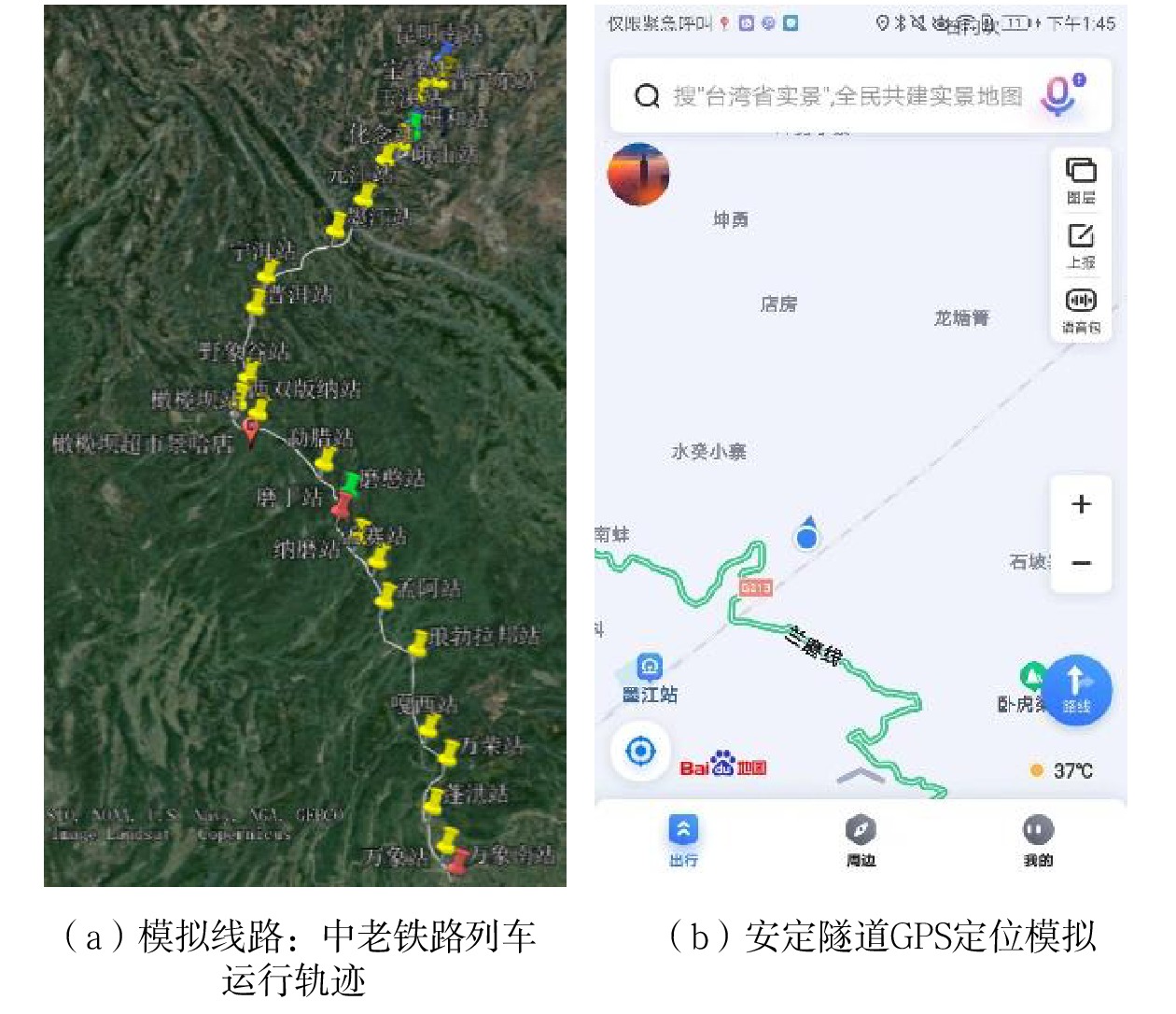
单点信息 可用卫星数量/颗 定位精度/ m 信噪比 最小值 最大值 峨山站 13 3 46 53 野象谷站 13 3 45 51 橄榄坝站 13 3 43 52 勐腊站 13 3 47 50 纳磨站 13 4 45 49 孟赛站 13 4 46 51 孟阿站 13 3 44 53 嘎西站 13 4 47 50 茂密森林区域 13 3 44 50 多山地带 13 4 43 52 普亚村隧道 13 4 45 51 努瓦山隧道 13 3 44 50 安定隧道 13 3 43 51 平均值 13 3.4 44.8 51 -
[1] 莫志松,安鸿飞. 新型列控系统列车综合自主定位技术研究[J]. 铁道学报,2022,44(1):56-64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.01.008 [2] 张辰东,王智新,李阳,等. 北斗定位技术在列控应用中的标准化研究[C]//第十三届中国卫星导航年会论文集—S10政策法规、标准化及知识产权,2022-05-25,中国北京,2022:7-12. [3] Jiang W, Yu Y Z, Zong K B, et al. A seamless train positioning system using a Lidar-aided hybrid integration methodology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(7): 6371-6384. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3080393
[4] Heirich O, Siebler B, Sand S, et al. Measurement methods for train localization with onboard sensors[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 European Navigation Conference (ENC), 23-24 November 2020, Dresden, Germany. New York, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1-10.
[5] Wu Y D, Weng J, Tang Z, et al. Vulnerabilities, attacks, and countermeasures in balise-based train control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(4): 814-823. DOI: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2590579
[6] Talvitie J, Levanen T, Koivisto M, et al. Positioning of high-speed trains using 5G new radio synchronization signals[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 15-18 April 2018, Barcelona, Spain. New York, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1-6.
[7] Yang M H, Liu J, Cai B G, et al. Research on integrity monitoring performance test method of GNSS-based train positioning units[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), 24-27 October 2018, Hangzhou, China. New York, USA: IEEE, 2018. 445-450.
[8] 帅玮祎,董绪荣,丛 蕾,等. 欧洲列控系统中GNSS应用研究与发展综述[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(7):1781-1789. [9] 刘 江,蔡伯根,王 剑. 基于卫星导航系统的列车定位技术现状与发展[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(11):4033-4042. [10] 鲍才让太. 青藏铁路列控系统国产化研究[J]. 铁道通信信号,2015,51(12):10-13. [11] 莫重明. 高原铁路信号系统列车自主定位方案选型研究[J]. 铁道通信信号,2020,56(7):11-14. [12] 我国首个地铁北斗定位系统开建 [J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2022,25(4):94. [13] 舒铭泽,江 珊,舒 鹏. 北京信息科技大学苏中教授团队:创新科技 做盲环境的“眼睛”[J]. 中国高新科技,2021(7):26-29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4137.2021.07.011 [14] 王 植,吴立新,孔祥勤. 盲环境移动定位(Ⅰ):序列编码图形路标识别算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2011,32(5):732-735. [15] 兰 蒙,邹劲柏,纪文莉,等. 基于软件无线电的LTE-M无线通信系统零现场测试[J]. 都市快轨交通,2022,35(6):151-157. [16] 毛 虎,吴德伟,卢 虎. GNSS信号体制抗干扰性能分析[J]. 电子科技大学学报,2020,49(4):575-583. DOI: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018168 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 熊磊. 基于BERT的中药材治疗胃病的命名实体识别. 软件导刊. 2025(01): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 甘进龙,刘青,黄小飞. 基于RoBERTa-CNN-BiLSTM-CRF的“数据结构”课程知识命名实体识别. 信息系统工程. 2024(07): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曾文驱,马自力,王淑营. 高速列车零部件知识图谱的智能问答知识子图匹配研究. 铁路计算机应用. 2023(12): 1-5 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: