Experimental data analysis and simulation on noise reduction optimization of roof structure beneath pantograph of high-speed multiple electric units
-
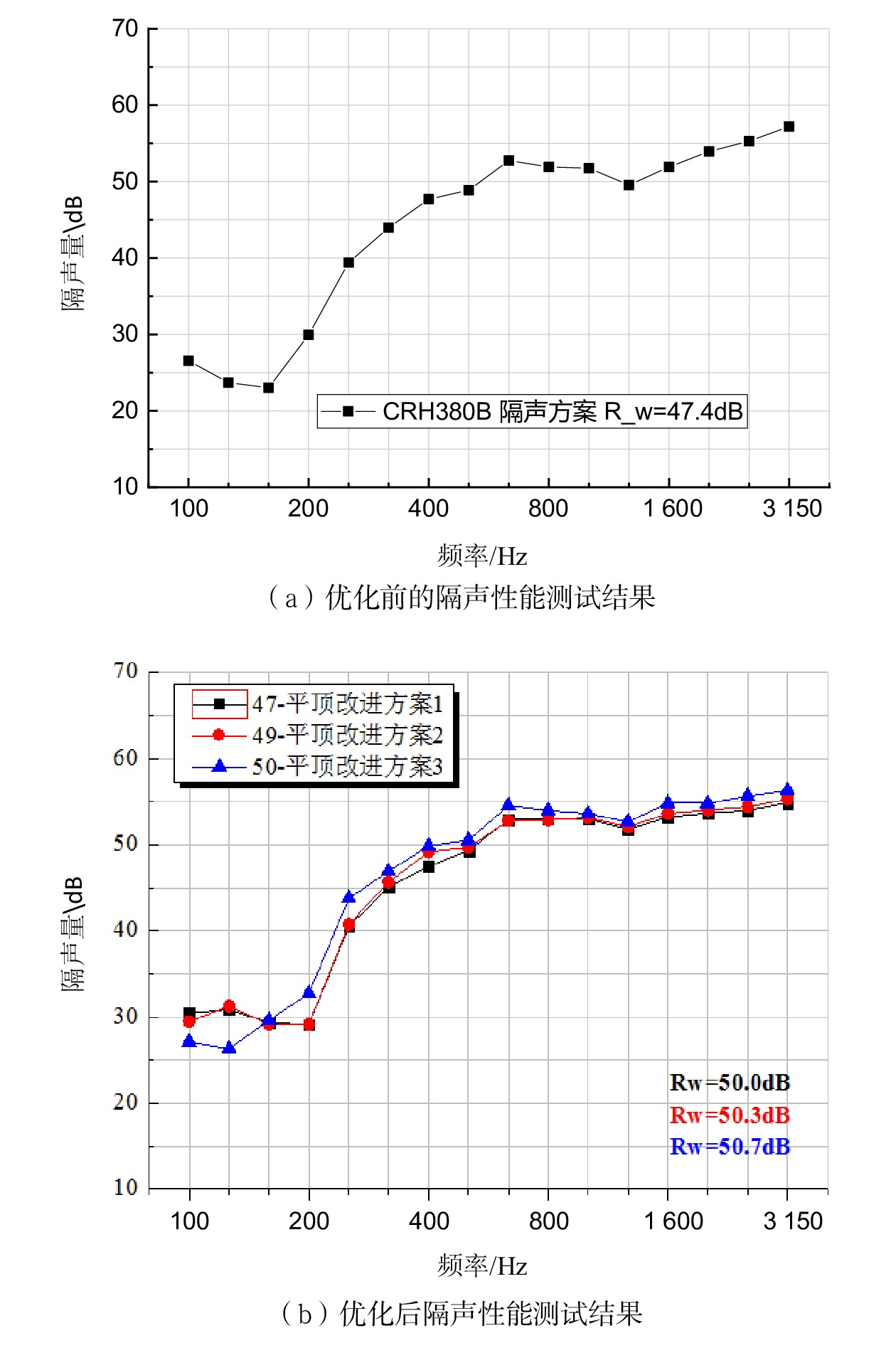
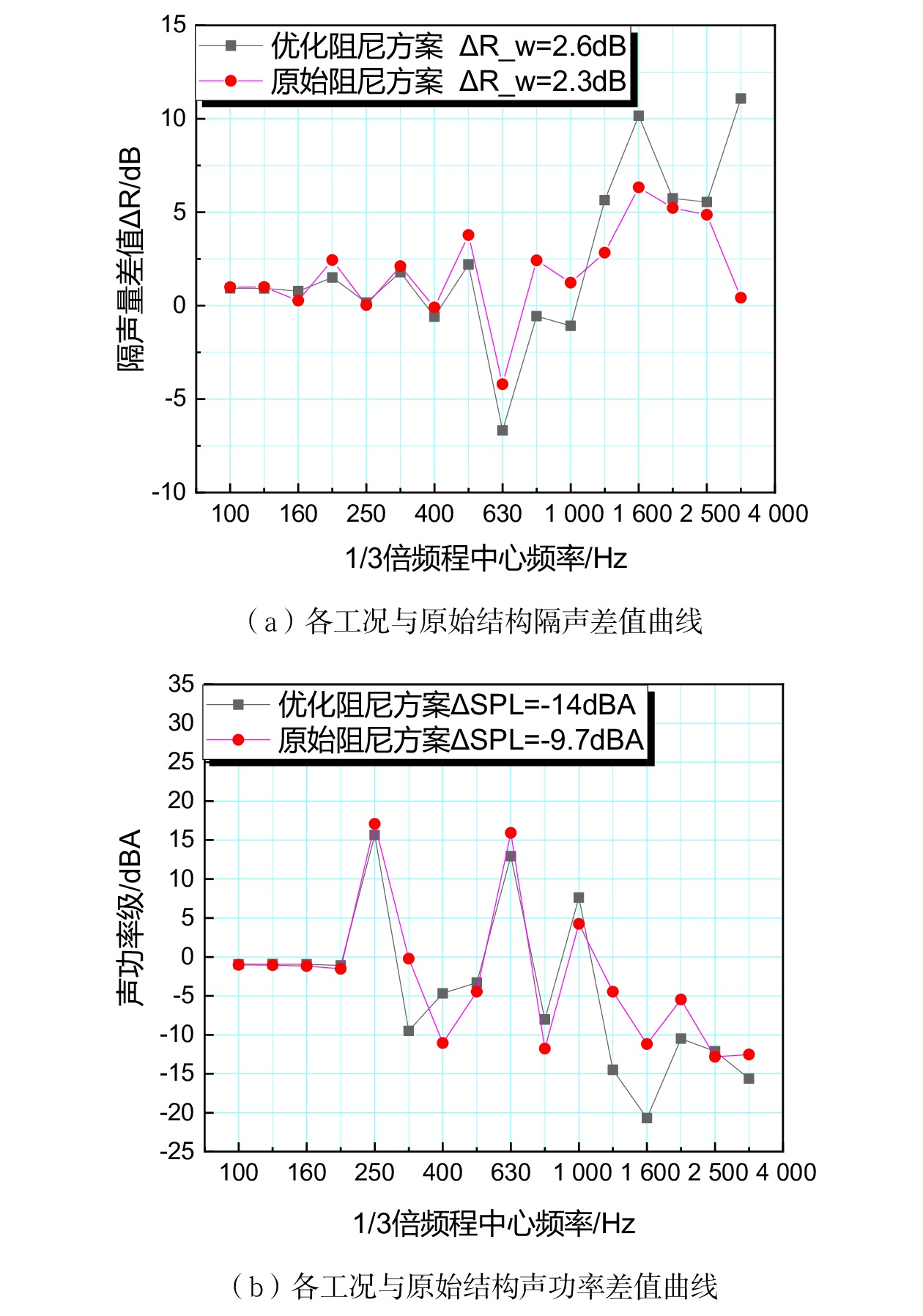
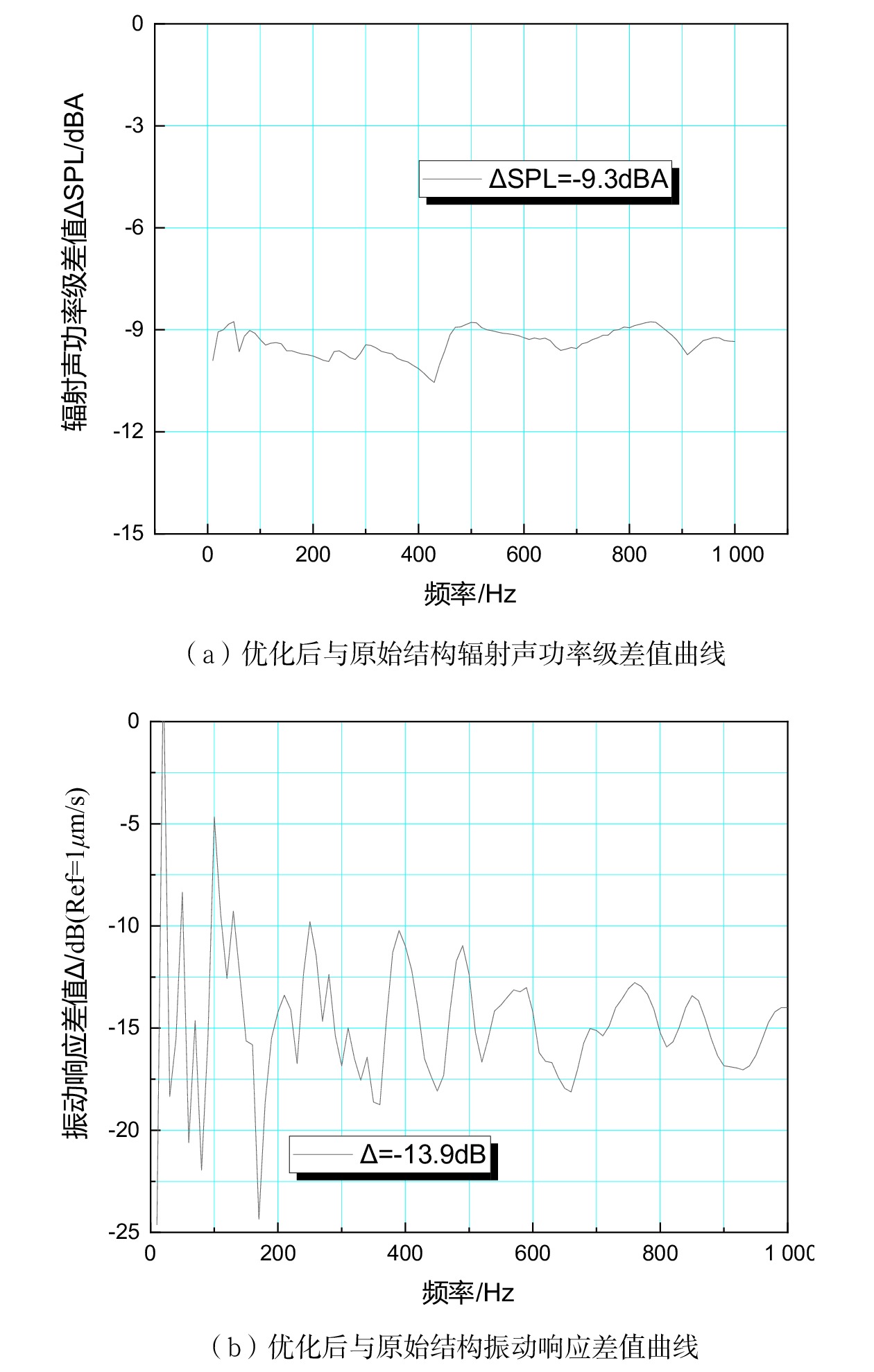
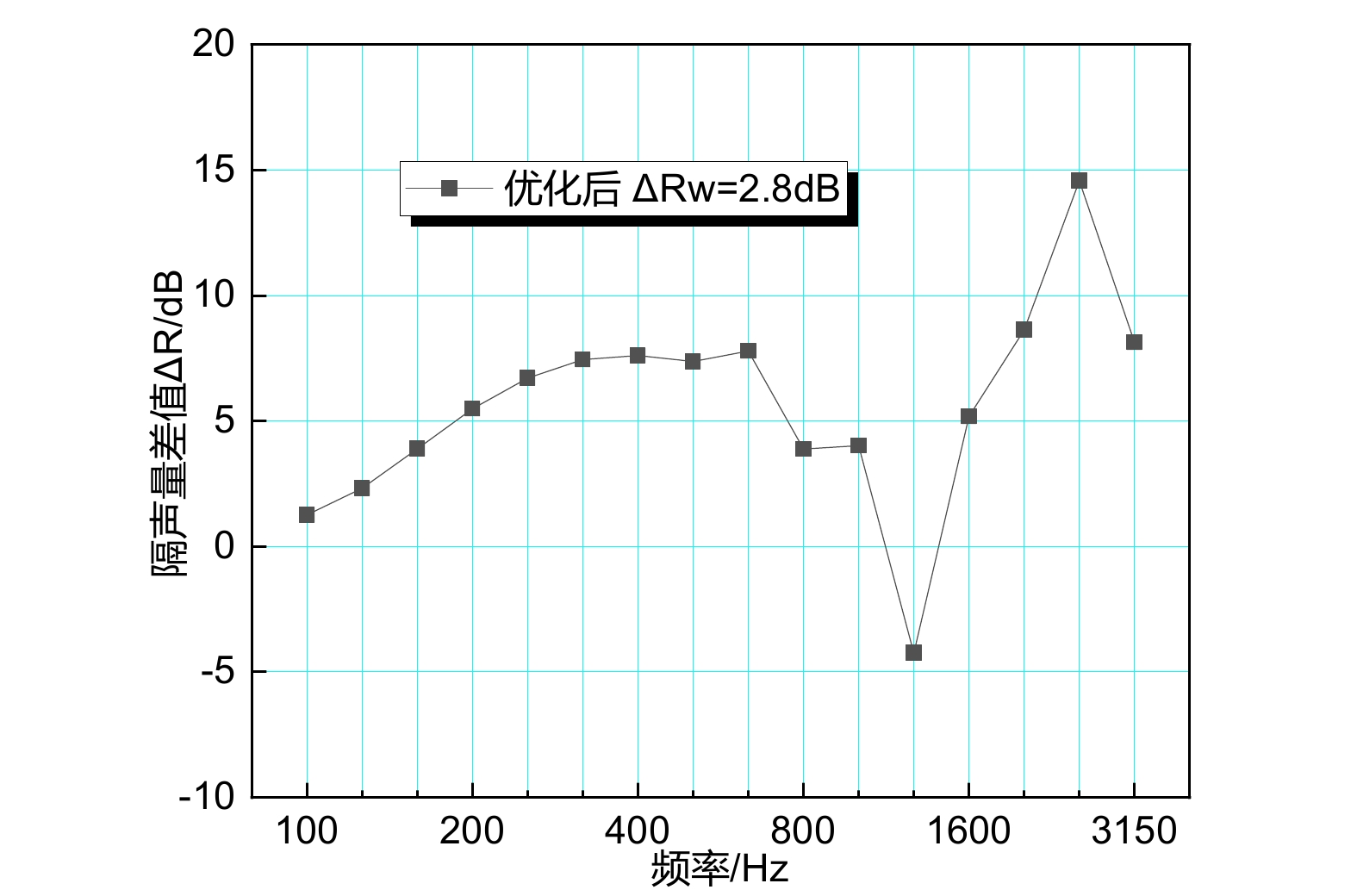
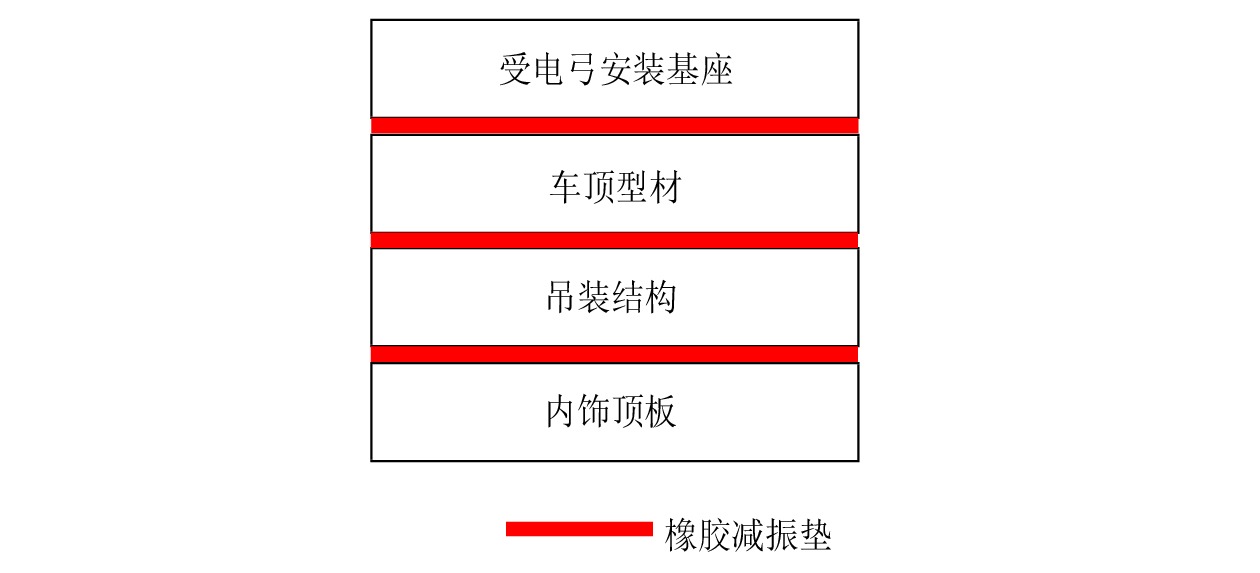
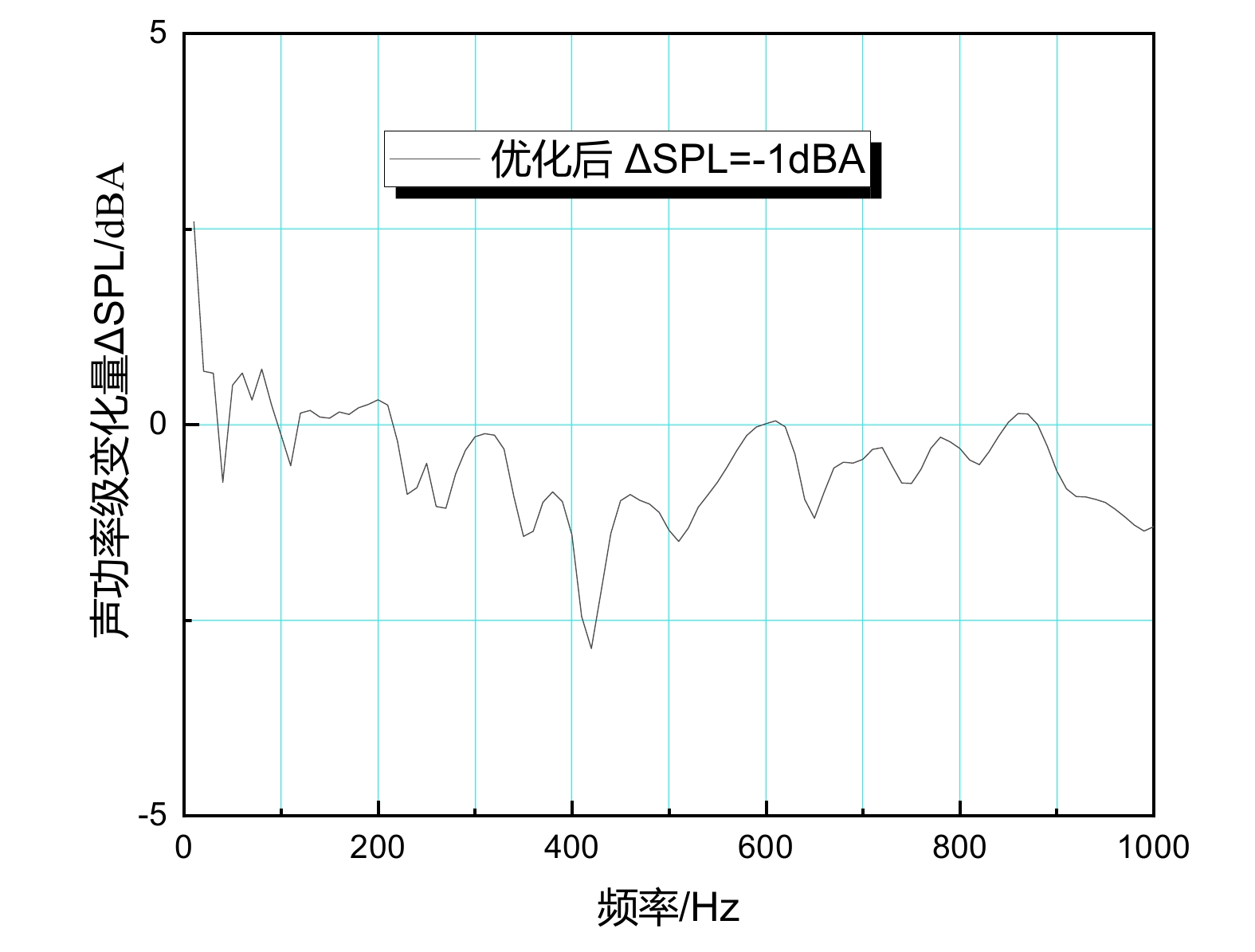
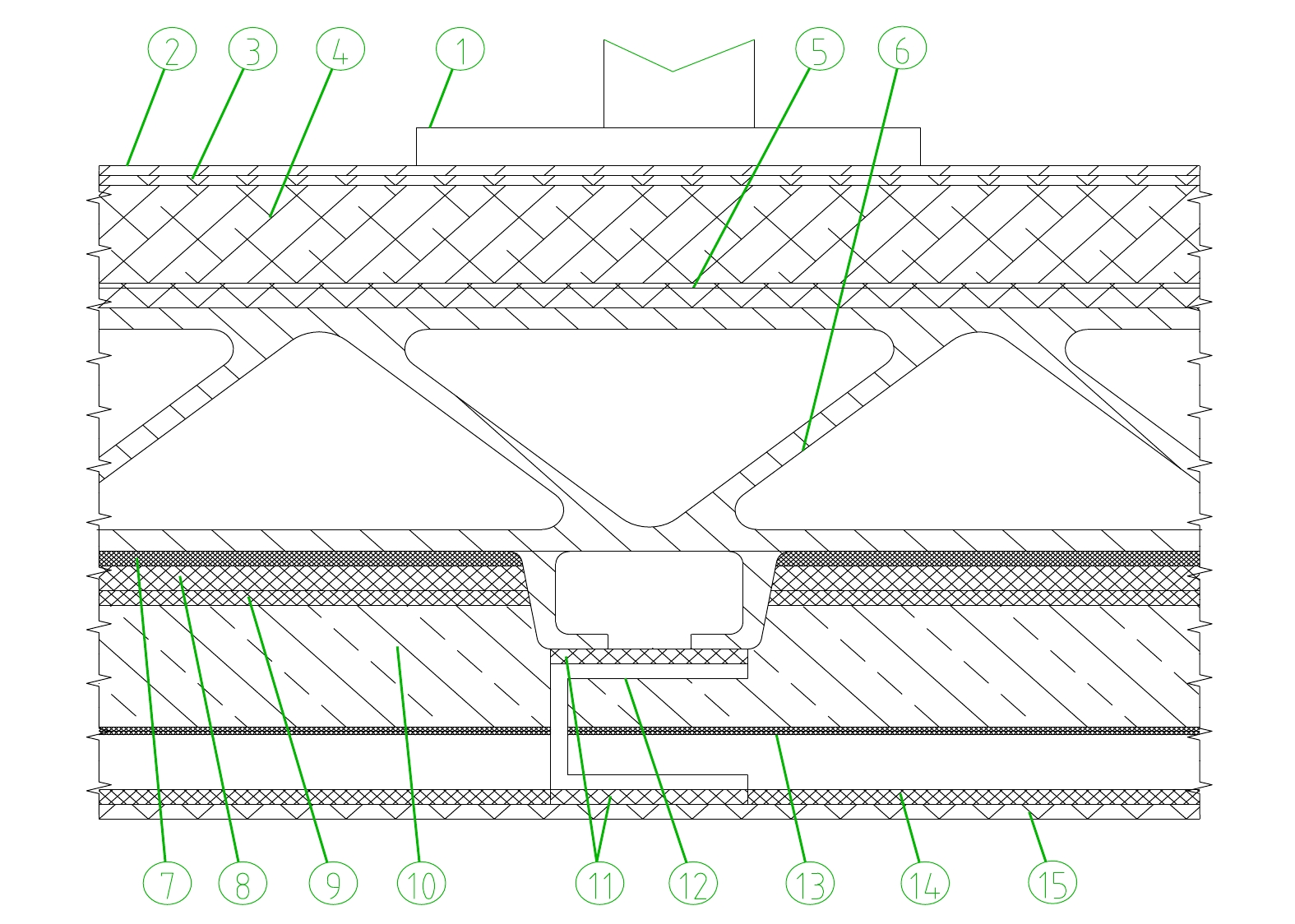
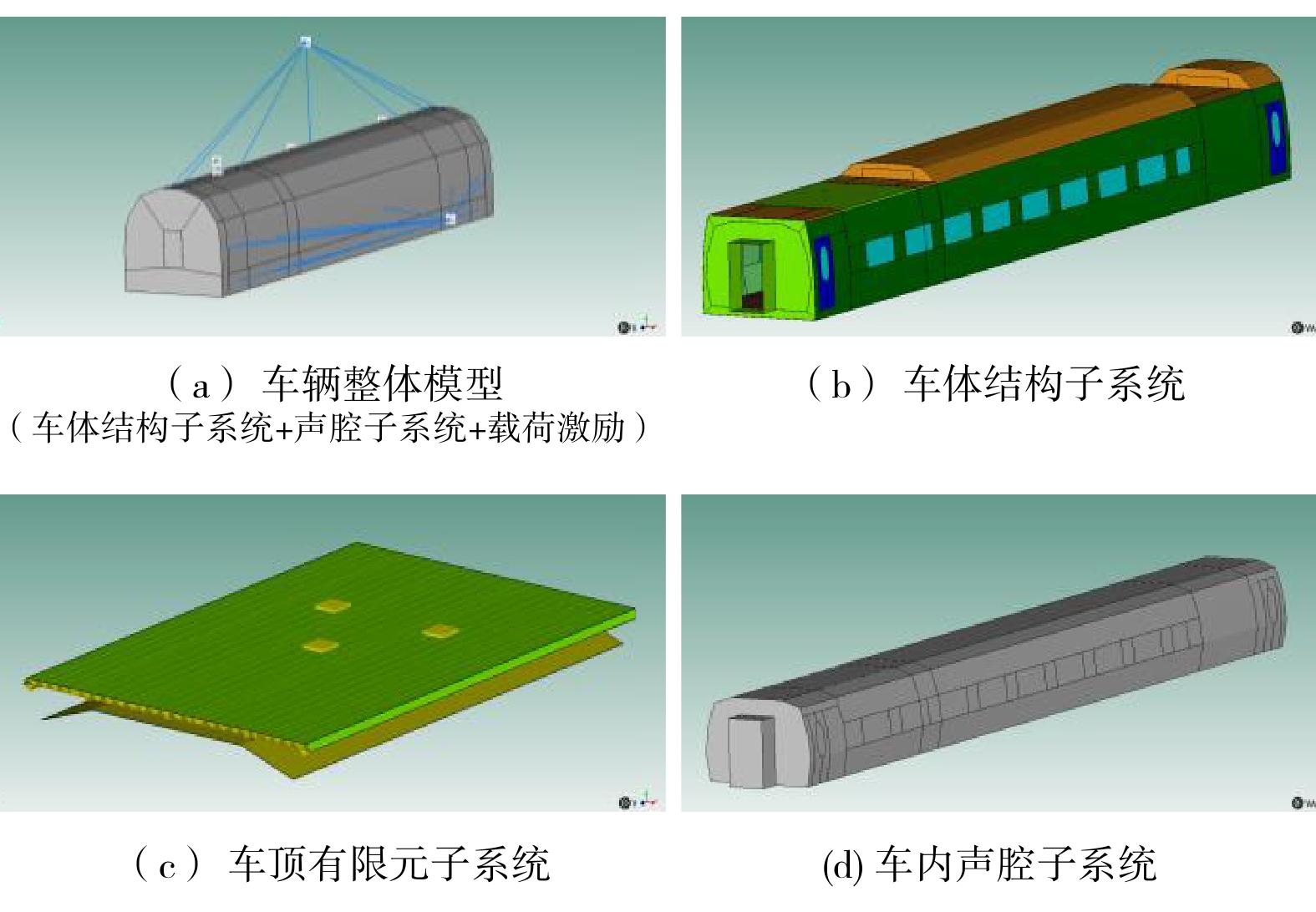
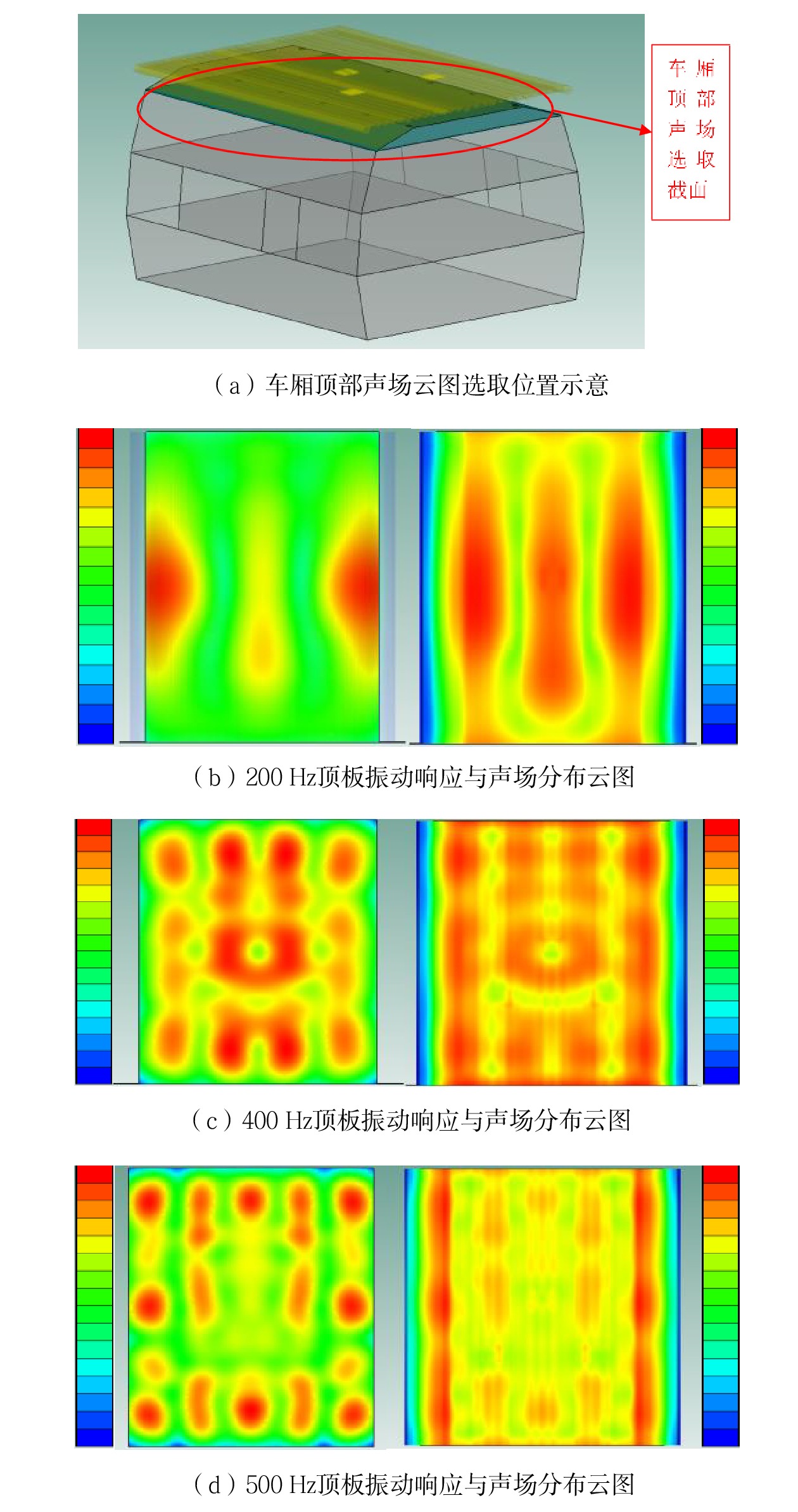
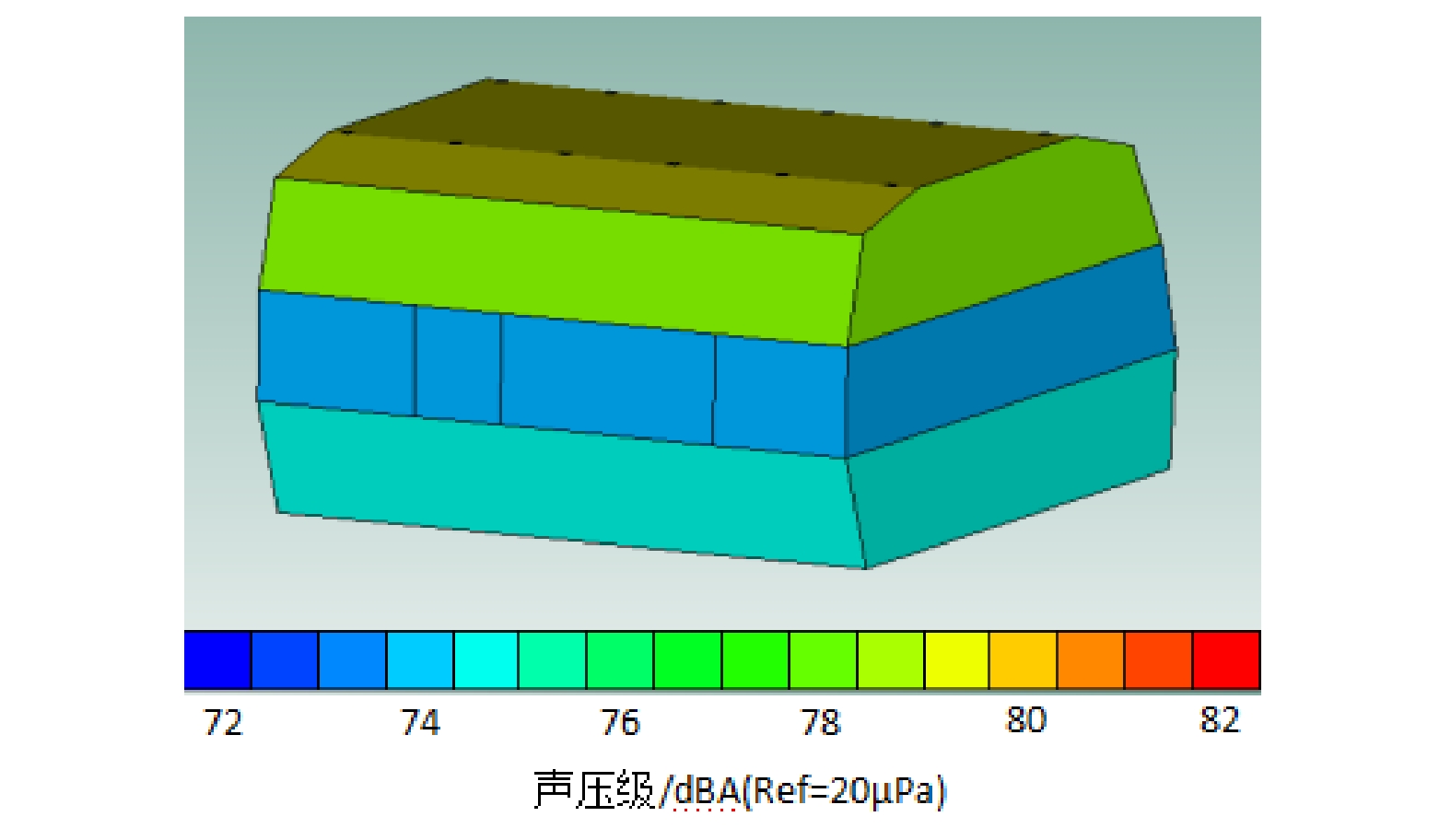
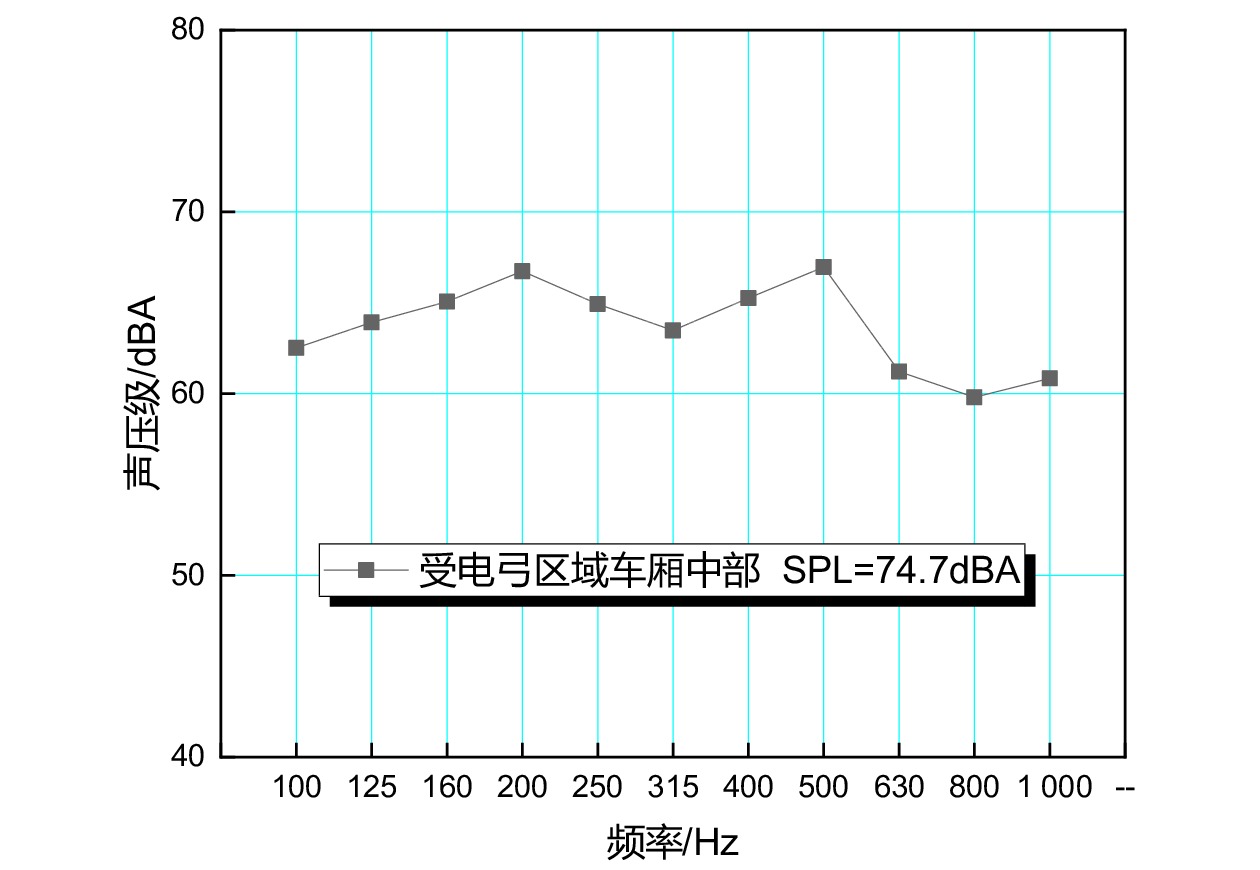
摘要: 当前我国高速动车组列车运行速度超过350 km/h,受电弓区域车顶结构产生的噪声已成为车厢内最大噪声源,影响乘客乘坐体验。文章采用试验数据分析与仿真方法,对CRH380B型和CR400BF型动车组受电弓区域车顶结构进行全路径降噪优化措施试验研究,包括顶板型材阻尼处理优化、车顶内饰板声辐射控制与结构优化、车体顶板组合结构吸声/隔声材料优化处理、顶板结构全路径结构传声控制优化;在考虑受电弓区域和转向架区域联合声振激励的前提下,采用FE-SEA法,基于优化后车顶结构的细节特征,建立整车车厢内噪声仿真模型,定量评估车顶结构各项降噪优化措施对车厢内噪声的改善效果。仿真结果表明:车顶结构降噪优化设计可使CRH380B型动车组受电弓区域下方车厢内噪声降低 3 dB,使CR400BF型动车组进一步降低1 dB以上。Abstract: At present, the running speed of Chinese high-speed Electric Multiple Units (EMUs) trains exceeds 350 km/h and the noise generated by the roof structure beneath the pantograph has become the largest noise source inside the carriage, affecting passengers' riding experience. The article adopts experimental data analysis and simulation methods to conduct experimental research on full path noise reduction optimization measures for the roof structure beneath the pantograph of CRH380B and CR400BF EMUs train, including optimization of damping treatment for roof profiles, control and structural optimization of sound radiation from roof interior panels, optimization of sound absorption/insulation materials for the combined structure of the roof, and optimization of sound transmission control for the full path structure of the roof structure. In consideration of the combination of the sound and vibration excitation from the pantograph and the bogie and based on the detailed characteristics of the optimized roof structure, the FE-SEA method is adopted to establish a noise characteristics simulation model of the entire vehicle compartment below the pantograph for quantitative evaluation of the improvement effects of noise reduction optimization measures of the roof structure on the noise inside the carriage. The simulation results show that the noise reduction optimization of the roof structure determined in this chapter reduces the noise inside the carriage below the pantograph of the CRH380B high-speed train by 3dB, and further reduces the noise of the CR400BF high-speed train by more than 1dB.
-
10 kV贯通(自闭)线负责为铁路沿途信号和通信等设备设施及其他铁路综合用电负荷(如沿线车站和生产生活部门)[1]供电,是铁路行车必不可少的装备。沿途供电负荷具有位置分散、地理分布广,贯通线呈现里程长、分枝多的特征[2]。而贯通线的带电情况,直接关系到铁路行车的正点运行和人员安全,是供电运行监控和管理的基本任务之一。
监测贯通线带电状态的常用方法,是用电压电流表进行指示,但是由于线路工作电压高达10 kV,需要先经过10 kV的电压和电流互感器,才能用电压电流表进行指示。显然,这样的方式不够便捷,且设备投资成本较大。随着计算机技术的应用,可在计算机上对贯通线带电状态进行可视化监控,按照实际供电接线图显示开关的分闸/合闸位置和特定位置的电压电流参数等[3-7]。
对于电气连接的导线、母排,特别是数十千米的贯通线,由于接线图形呈线状,各点位置的电压电流不同,无法密集地用电压和电流互感器来采样显示。如果采用深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索等算法[8-11]来递归和回溯判断贯通线的带电状态,除需配置10 kV电压和电流传感器外,计算中每一步都需要遍历整个供电网络(简称:电网)的拓扑连通结构,占用计算机内存较大,运行耗时较长,效率不高。
为在贯通线的计算机监控中快速显示线路的带电状态,方便用户直观了解线路、导线和有关设备的带电状态,减少计算机监控内存占用率和搜索量,提高工作效率,本文研究一种色流算法,基于电流的流向和通道,在计算机监控屏上直观显示贯通线及相关的开关、变压器等设备的带电状态。
1 铁路电网类型与特征
从铁路电力供电的任务和网络结构分析,电网可分为放射性结构电网和环状结构电网。
1.1 放射性结构电网
放射性结构电网通常采用单电源,通过在线路上设置大量的高压开关,控制各个用电部门的停电/送电,电网呈辐射状,具有里程长、分枝多的结构特点,各用电点之间互不影响,主要用于某一区域内生产、生活类供电。
1.2 环状结构电网
环状结构电网主要为供电可靠性要求较高的一级负荷进行供电,一般情况下采用双电源供电,或采用单电源的不同母线向环状线路的首尾同时供电。铁路车站的指挥和信号等设备设施的供电,不仅直接关系到行车的正点和经济效益,更涉及列车运行安全和旅客的人身安全。贯通线是一级负荷,采用双电源结构,线路上各个供电节点的控制开关采用“手拉手”方式连接,保证线路故障时仍能获取电能,进而保障行车指挥和信号设备设施的不间断供电。
2 色流算法
2.1 色流定义
在铁路供电监控管理中,为了实时、动态反映贯通线的带电状态,在不采用电压和电流互感器进行监测的条件下,较简单、可靠的带电状态识别方法是:根据电流流动的路径进行判定,有电流流动的线路或设备就会带电工作。将配电所的母线视为电源,从母线开始搜索,如果与母线连接的开关闭合,电流就会通过开关,流向开关的非母线侧线路,从而判定该线路带电;如果与母线连接的开关断开,电流就不会通过,进而判定开关的非母线侧线路不带电,其它线路或设备的带电状态也可以此类推。
综上,采用计算机监控供电线路及设备带电状态时,可利用红色(带电状态)和绿色(停电状态)2种颜色,基于可视化图形,直观地表达线路或设备的带电/停电状态。本文在贯通线带电状态监控中,将电流的流动用色流来定义和表达。将配电所母线视为抽象的色流源,供电线路视为色流管,供电的控制开关视为色流阀。按照色流定义,从色流源开始搜索,只要与色流源连接的色流阀处于打开(开关闭合)状态,就判定色流(电流)通过,与色流阀出口连接的色流管(线路和线路上连接的设备)染色为红色,以表示带电。同理,与红色的色流管连接的下一个色流阀打开,即判定色流通过,下一级色流管自动染为红色,并以此类推。反之,若色流阀关闭或色流阀入口的色流管非红色,则下一级色流管染为绿色,表示不带电。
2.2 单电源供电模式的染色
在利用色流算法对供电线路带电状态进行搜索与染色的过程中,还需定义色流阀的入口和出口。在高压供电控制中所有的开关电流都是一进一出的结构,因此,色流算法中的色流阀也采用一进一出的结构,如图1所示。
本文用
${{{L}}_{{i}}}$ 表示序号为${{i}}$ 的色流管;${{{S}}_{{j}}}$ 表示序号为${{j}}$ 的色流阀;${{{X}}_{{i}}}{{(k)}}$ 表示色流管${{{L}}_{{i}}}$ 连接的色流阀序列,${{k}}$ 为序列中的色流阀总数;${\rm{Red(}} \cdot {\rm{)}}$ 变量表示色流管或色流阀染色是否为红色,若为红色则${\rm{Red(}} \cdot {\rm{)}}$ =1,若为绿色则${\rm{Red(}} \cdot {\rm{)}}$ =0。色流网络中任何一条色流管
${{{L}}_{{{i + }}1}}$ 是否染成红色,由其连接的色流阀的开闭状态以及色流阀上一级的色流管的染色状态共同决定,其数学表达式为:$${\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_{{{i}} + 1}}) = {\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_{{i}}}) \wedge {{\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_{{j}}})} $$ (1) 将公式(1)应用到放射性结构电网中搜索并判断线路的带电状态。在如图2所示,放射性结构电网中,线路
${{{L}}_{\rm{4}}}$ 从配电所母线获取电能的供电路径上包含有开关${{{S}}_1}$ 、${{{S}}_2}$ 、${{{S}}_4}$ 及线路${{{L}}_1}$ 、${{{L}}_2}$ 。其中,色流管
${{{L}}_{\rm{4}}}$ 连接的色流阀序列为${X_4}(3) = $ $ \{ 1,2,4\} $ ,基于公式(1),线路${{{L}}_{\rm{4}}}$ 带电状态的染色表达式为:$$\begin{aligned} {\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_4}) &= {\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_2}) \wedge {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_4})\\ &= {\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_1}) \wedge {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_2}) \wedge {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_4})\\&= {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_1}) \wedge {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_2}) \wedge {\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_4})\\&= \prod\nolimits_{{{j}} \in {{{X}}_4}(3)} {{\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_1})} \end{aligned}$$ (2) 采用归纳法,单电源供电模式下供电线路带电状态的搜索与染色算法,可以表示为:
$${\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_{{i}}}) = \prod\nolimits_{{\rm{j}} \in {{\rm{X}}_{\rm{i}}}({\rm{k}})} {{\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_{{j}}})} ,1 \leqslant {{i}} \leqslant {{n}}$$ (3) 其中,n表示色流管的最大序号。
2.3 双电源供电模式的染色
双电源供电模式下的供电线路可以从2个方向获取电能。在色流算法中,将连接2个配电所的母线(或同一个配电所的2个不同母线)定义为2个色流源,其它的搜索和判定步骤与单电源供电模式色流算法类似。
对于双电源供电线路,
${{X}}_{{i}}^1({{k}}){\text{、}}{{X}}_{{i}}^2({{k}})$ 分别表示色流管${{{L}}_{{i}}}$ 在2个方向上的色流阀序列,带电状态的搜索与染色算法可以表示为:$$\begin{aligned} & \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!{\rm{Red}}({{{L}}_{{i}}})\!\! =\!\!\left(\prod\nolimits_{{{j}} \in {{X}}_{{i}}^1({{k}})} {{\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_{{j}}})} \right) \vee \left(\prod\nolimits_{{{j}} \in {{X}}_{{i}}^2({{k}})} {{\rm{Red}}({{{S}}_{{j}}})} \right), \\& \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!1 \leqslant {{i}} \leqslant {{n}} \end{aligned}$$ (4) 3 带电状态监控与实现
3.1 监控装置构成和工作过程
监控铁路贯通线带电状态装置的主要硬件设备为:服务器和开关状态采集器;主要软件包括:SQL Server数据库、VS 2010可视化人机交互程序、带电搜索与分析程序。本文采用VB.NET技术,应用VB编程语言开发。监控装置的工作过程为,开关状态采集器实时采集铁路贯通线上开关的分合闸状态数据信息,并将其上传至服务器,同时,SQL Server数据库实时更新开关状态信息;带电搜索与分析程序根据上传的信息快速完成线路带电状态的判断,VS 2010可视化人机交互程序对线路进行染色处理,将带电状态直观显示在显示器上。
3.2 色流算法的程序设计
贯通线带电状态监控的核心任务,是通过计算机程序自动实现对贯通线开关状态的搜索、带电分析判断、线路染色。按照色流算法,可以分为2步:(1)完成各开关和分段线路的带电状态搜索、分析与判断,如图3所示;(2)完成线路的染色。
为直观展示贯通线的带电状态,本文分别用VS 2010工具箱中的RectangleShape、LineShape控件来表示开关和分段线路,利用控件的颜色属性来标识开关、线路的带电/停电状态,如表1所示,相应的染色步骤实现流程如图4所示。
表 1 控件颜色属性设置名称 类型 状态 颜色 BorderColor FillColor BackColor 开关 RectangleShape 合闸 Red Red Red 分闸 Green Gainsboro Green 线路 LineShape 带电 Red / / 停电 Green / / 3.3 应用
本文将带电状态监控装置应用到了麻城—黄陂贯通线的运行监控当中,监控界面如图5所示,其中,红色线段和设备是带电运行的,绿色线段和设备为停电状态。如果运行中麻城—黄陂贯通线上任一个开关分合闸变位,界面经过0.1 ms响应(数据采集器的响应时间),即刻动态地反映线路与设备的带电状态变化。
由于监控屏可直观展示麻城至黄陂贯通线各分段线路和设备的带电情况,以及为相关车站供电的运行情况,显著地提高了供电管理自动化程度和工作效率。例如,图5中显示麻城—黄陂贯通线的甘露山箱式变压器(简称:箱变)处于停电检修状态,检修车间人员可以及时从监控屏上查看到,从而尽早做好检修准备,提高工作效率。
4 结束语
利用色流算法对贯通线及设备进行带电状态搜索、判断与染色,从而对贯通线带电状态进行监控,不需使用电压和电流互感器采集监控线路的电压电流,且与深度优先、广度优先等搜索算法相比,不需遍历整个电网。因此,该方法能显著简化监控装置的硬件配置,节省监控装置的投资成本;占用计算机内存少,计算简单,运行速度快,可实时、动态地反映线路和设备的带电情况,监控效率更高、效果更好。
-
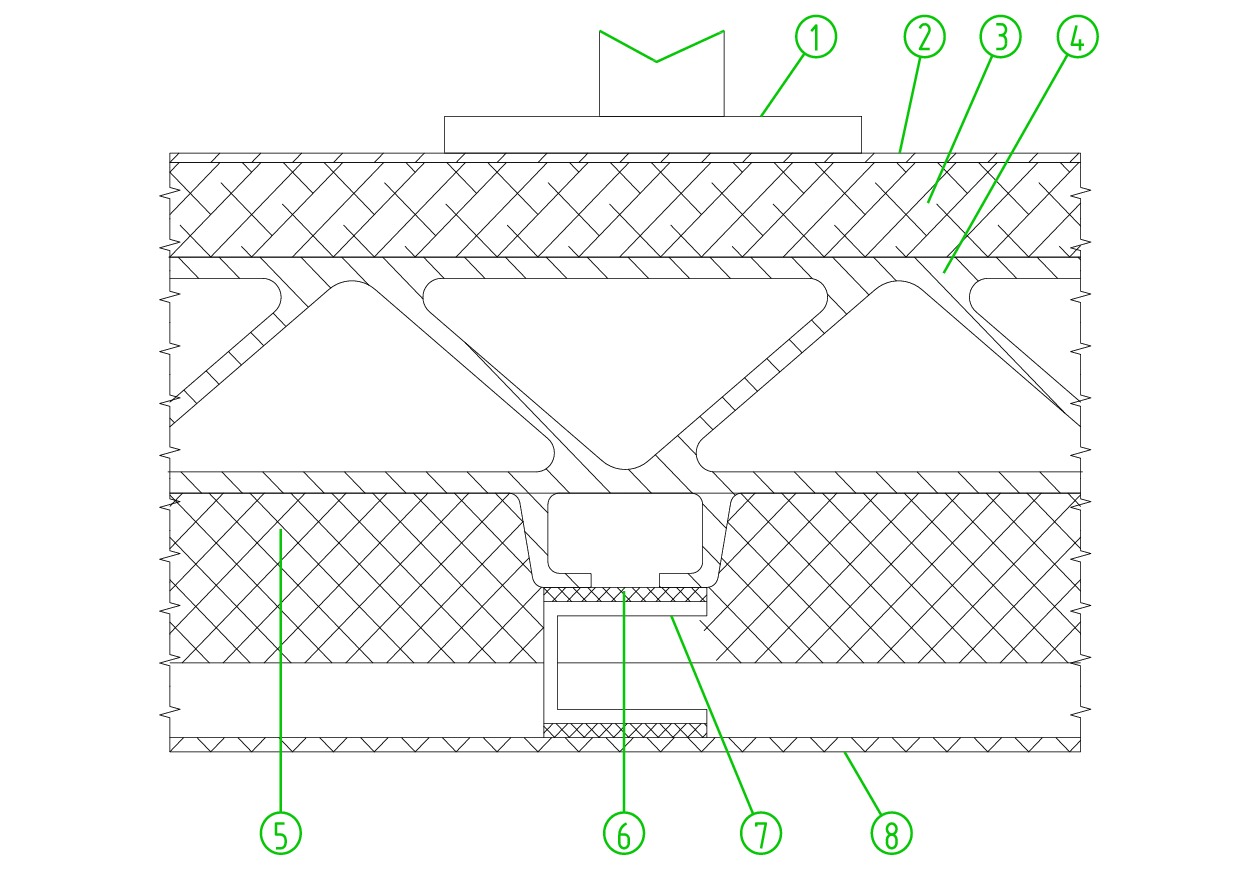
表 1 吸声/隔声优化措施
材质种类 优化措施 吸音材 加厚4 mm 玻璃棉板 加厚5 mm,铺设位置由两层防火隔音毡之间改为两层防火隔音毡之上 隔音垫 密度Ρ减小200 kg/m3;弹性模量E加大450 Mpa 表 2 仿真中定义的动车组列车不同运行速度工况
序号 运行工况 1 160 km/h匀速 2 200 km/h匀速 3 250 km/h匀速 4 300 km/h匀速 5 350 km/h匀速 表 3 优化措施对应的不同工况条件
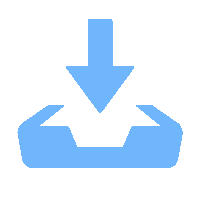
工况编号 计算条件 工况1 原始工况 工况2 阻尼处理优化上 工况3 隔声处理优化 工况4 全路径结构声优化 工况5 内饰顶板优化 工况6 整体优化 -
[1] 谭晓明,杨志刚,吴晓龙,等. CIT500车外噪声源频谱分解模型的试验研究[J]. 铁道学报,2017,39(7):32-37. [2] Tan X M, Yang Z G, Tan X M, et al. Vortex structures and aeroacoustic performance of the flow field of the pantograph[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 432: 17-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.06.025
[3] 廖 欣,梁君海,孙召进,等. 受电弓对高速列车噪声的影响[J]. 声学技术,2011,30(4):171-174. [4] 张淑敏,史佳伟,圣小珍. 受电弓区域气动激励特性及其对车内噪声的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(3):258-268. [5] 郭建强,葛剑敏,张华丽. 高速列车受电弓区车内噪声研究与控制[J]. 振动、测试与诊断,2017,37(4):662-666. [6] 廖欣,梁君海,孙召进,等. 受电弓对高速列车噪声的影响[C]//2011中国西部声学学术交流会论文集,2011-08-17,银川. 上海:《声学技术》编辑部,2011. [7] 伏蓉,张捷,姚丹,等. 高速列车车体轻量化层状复合结构隔声设计[J]. 噪声与振动控制 ,2016(1):48-52. [8] 张捷,肖新标,王瑞乾,等. 高速列车铝型材声振特性测试及等效建模[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版) ,2017(3): 545 -553.





 下载:
下载: